If you are searching for 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers, chances are you are working through a programming module and want clarity, not just a copied solution. While it can be tempting to look for quick answers, understanding the logic behind the exercise is what truly strengthens your coding skills. This in-depth guide explains the structure, programming concepts, and problem-solving techniques involved in 9.7.4 Leash on CodeHS, helping you complete the assignment confidently and correctly.
Rather than providing a simple copy-paste response, this article breaks down the concepts typically used in the Leash exercise, including object references, parameters, class interaction, and event-driven programming. By the end, you will understand how to approach similar problems independently.
Understanding CodeHS and Its Learning Environment
CodeHS is an online computer science education platform designed to teach programming through interactive lessons and practical exercises. It is widely used in schools across the United States and internationally. The platform supports languages such as JavaScript, Python, Java, and others.
Exercises like 9.7.4 Leash are typically part of a structured curriculum. By the time students reach section 9.7.4, they are usually working with more advanced concepts involving objects, classes, or graphical simulations.
When students search for 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers, what they often need is help understanding how objects communicate or how to control behavior dynamically within a program.
Also Read:Viltnemnda: Norway’s Local Wildlife Management Authority Explained
What Is the 9.7.4 Leash Exercise About?
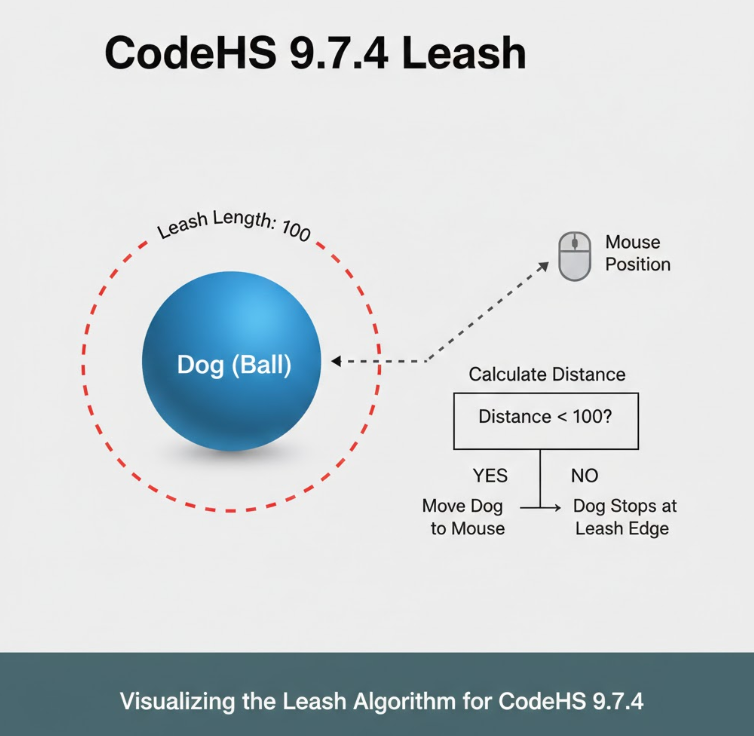
The Leash exercise generally focuses on object relationships. In many versions of the assignment, you create an object that follows another object, similar to how a dog follows its owner on a leash. The purpose is to simulate dependency between objects using programming logic.
The core learning objective typically involves:
Understanding object instantiation
Using parameters within constructors
Updating object positions dynamically
Connecting one object’s behavior to another
The “leash” metaphor helps students visualize how one object’s position or state depends on another. Instead of acting independently, the second object references the first object’s coordinates or movement logic.
When looking for 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers, you are really trying to understand how this relationship is coded.
Key Programming Concepts Behind 9.7.4 Leash CodeHS Answers
Object-Oriented Programming Foundations
By section 9.7.4, students are usually working with object-oriented programming principles. These include:
Classes and constructors
Instance variables
Methods
Object references
The Leash exercise demonstrates how one object can “know about” another object. This requires passing references correctly and storing them as properties inside the dependent object.
Instead of creating two completely separate objects, the leash object needs access to the main object’s position.
Position Tracking and Dynamic Updates
In many CodeHS graphical exercises, objects exist in a coordinate system. Each object has an x and y position. To simulate a leash, the dependent object often updates its position based on the primary object’s location.
For example, if the owner moves right, the dog must also move right, maintaining a certain distance.
This teaches:
Real-time updates
State synchronization
Event-driven programming
Understanding this logic is crucial to solving 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers correctly.
Step-by-Step Conceptual Breakdown of the Leash Logic
Instead of copying code, let’s explore the reasoning process.
First, you create the primary object. This could represent a person or another graphical entity. It contains properties such as x and y coordinates and possibly a move function.
Second, you create a secondary object that represents the leashed object. This object takes the first object as a parameter. Instead of storing static coordinates, it stores a reference to the primary object.
Third, inside the update method of the leashed object, you set its position relative to the main object. For example, the x position might be set to the owner’s x position minus a fixed distance.
Fourth, you ensure that the update function runs continuously or whenever movement occurs.
This logical structure is the core idea behind 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers.
Also Read:Xenoblade Chronicles X Definitive Edition XE Dom Jet Black Crest The Complete In-Depth Guide
Common Mistakes Students Make
Many students struggle with reference handling. Instead of storing a reference to the main object, they copy the coordinates once and never update them. This causes the leash effect to fail.
Another common issue is forgetting to call the update method inside the animation loop. Without repeated updates, the leashed object remains static.
Students also sometimes misuse scope. If variables are declared incorrectly, the dependent object cannot access the primary object’s properties.
Understanding these common pitfalls makes it easier to solve 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers independently.
Real-World Application of the Leash Concept
The leash concept is not just academic. It is used in game development and simulations. Many video games feature companion characters that follow the player. These companions rely on position tracking logic similar to the 9.7.4 Leash exercise.
In robotics, tracking systems use sensor data to maintain relative positioning. In animation, parent-child relationships determine how objects move together.
Learning the logic behind 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers builds foundational knowledge for these advanced applications.
Why Copying Answers Is Not Effective
Searching directly for 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers may provide code snippets online, but copying them limits learning. Programming is cumulative. Each concept builds on previous understanding.
If you skip comprehension at this stage, later modules involving inheritance, complex object interactions, or game physics become significantly harder.
Instead of copying, focus on:
Understanding object references
Testing incremental changes
Debugging logically
Reading error messages carefully
Mastering these skills helps beyond this single assignment.
Debugging Strategies for the Leash Exercise
Debugging is part of professional software development. When your leash logic fails, approach it systematically.
Check whether the primary object is moving correctly. If it is not updating positions, the dependent object cannot follow.
Verify that the reference to the primary object is stored properly in the constructor.
Confirm that the update method runs consistently.
Print coordinate values temporarily to see if they change over time.
These strategies help you correct your 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers without external help.
Also Read:3840 x 1240 Naruto x Boruto Ultimate Banner The Complete Ultra-Wide Guide
Improving Your Understanding of Object Relationships
Object relationships are central to modern programming. The Leash exercise introduces association, where one object uses another but does not inherit from it.
Later, you may learn about composition and inheritance. Understanding association through exercises like 9.7.4 strengthens your foundation.
When students repeatedly practice linking object behaviors, they develop an intuitive understanding of how complex systems are structured.
Performance and Optimization Considerations
While 9.7.4 Leash is a beginner-level exercise, it introduces important efficiency principles.
Constant updates should be lightweight. Avoid recalculating unnecessary values. Keep update methods concise.
In large-scale applications, inefficient tracking logic can slow performance. Learning efficient update cycles early prepares you for advanced development.
Academic Integrity and Responsible Learning
Educational platforms like CodeHS emphasize integrity. Searching for 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers is understandable when stuck, but it is important to use guidance responsibly.
Use explanations as learning aids. Rewrite solutions in your own words. Test variations. Explore what happens when you change distances or movement speed.
This active engagement deepens retention and builds genuine programming competence.
Expanding Beyond the Assignment
After mastering the leash concept, try extending the project.
Add smooth interpolation so the follower gradually catches up.
Create multiple followers chained together.
Introduce variable leash lengths.
Experiment with curved motion paths.
By expanding creatively, you transform a simple exercise into a mini simulation project.
Conclusion
Understanding 9.7.4 leash CodeHS answers goes far beyond completing a single assignment. The exercise introduces critical object-oriented programming concepts that form the foundation for game development, simulation design, and advanced software engineering.
By focusing on logic instead of copying code, you build lasting technical skills. Object references, dynamic updates, and state synchronization are powerful tools in any developer’s toolkit.
If you approach the problem methodically, debug carefully, and experiment creatively, you will not only complete the exercise successfully but also gain deeper confidence in your programming abilities.
FAQs
What programming language is used in 9.7.4 Leash?
It often depends on the course track. Many students complete it in JavaScript within the graphics module, though some variations may appear in other languages.
Why does my leashed object not move?
This usually happens because the update function is not called continuously, or the object reference was not stored correctly.
Can I modify the leash distance?
Yes. The offset between objects can be adjusted to simulate different leash lengths.
Is there only one correct solution?
No. As long as the dependent object follows the primary object correctly, multiple logical implementations are valid.
For more updates visit: blogify News

